| [1]Huang Y, Gloviczki P, Noel AA,et al.Early complications and long-term outcome after open surgical treatment of popliteal artery aneurysms: is exclusion with saphenous vein bypass still the gold standard? J Vasc Surg. 2007;45(4):706-713.[2]Heyligers JM, Lisman T, Verhagen HJ,et al.A heparin-bonded vascular graft generates no systemic effect on markers of hemostasis activation or detectable heparin-induced thrombocytopenia-associated antibodies in humans.J Vasc Surg. 2008;47(2):324-329.[3]Martelli E, Ippoliti A, Ventoruzzo G,et al.Popliteal artery aneurysms. Factors associated with thromboembolism and graft failure.Int Angiol. 2004;23(1):54-65.[4]李辉,陈群清,李少彬,等.改良小口径人工血管的血液相容性研究[J].中国医学创新,2013,15:10-12.[5]陆树洋,孙晓宁, 张鹏,等.层层自组装肝素/胶原复合涂层聚四氟乙烯小口径人工血管的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(4): 589-591.[6]李少彬,闫玉生,李辉,等. 等离子体磺酸化丝素蛋白膜聚四氟乙烯复合小口径人工血管的制备[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(8): 1357-1360.[7]王聪.细菌纤维素涂层的小口径人造血管研究[D].东华大学, 2012.[8]Pan L, Pei X, He R,et al.Multiwall carbon nanotubes/polycaprolactone composites for bone tissue engineering application.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;93:226-234.[9]Kawahira Y, Nishigaki K, Ueno T.Extracardiac Fontan procedure bridging the vertebra for apico-caval juxtaposition. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;82(1):350-352.[10]Chen ZG, Wang PW, Wei B,et al.Electrospun collagen-chitosan nanofiber: a biomimetic extracellular matrix for endothelial cell and smooth muscle cell.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(2):372-382.[11]Chen R, Qiu L, Ke Q,et al.Electrospinning thermoplastic polyurethane-contained collagen nanofibers for tissue-engineering applications.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2009;20(11):1513-1536. [12]Huang C, Chen R, Ke Q,et al.Electrospun collagen-chitosan-TPU nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineered tubular grafts.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011;82(2):307-315.[13]Chen R, Huang C, Ke Q,et al.Preparation and characterization of coaxial electrospun thermoplastic polyurethane/collagen compound nanofibers for tissue engineering applications.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2010; 79(2):315-325. [14]Su Y, Li X, Liu Y,et al.Encapsulation and Controlled Release of Heparin from Electrospun Poly(L-Lactide-co-epsilon- Caprolactone) Nanofibers.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2010. [Epub ahead of print][15]Yan S, Xiaoqiang L, Shuiping L,et al.Controlled release of dual drugs from emulsion electrospun nanofibrous mats.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2009;73(2):376-381.[16]隋景晗. 静电自组装糖胺聚糖抗体血管支架涂层的研究[D].大连理工大学.2008.[17]陈斌.肝素壳聚糖自组装表面修饰小口径涤纶人工血管的研究[D].复旦大学.2008.[18]Vloeberghs M, Hatfield F, Daemi F,et al.Soft tissue rapid prototyping in neurosurgery.Comput Aided Surg. 1998; 3(2):95-97.[19]Sun J, Xiong YY, Zhang FQ,et al.A preliminary study on maxillofacial prosthesis using structured light three-dimensional scanning and rapid prototyping technique.Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007; 42(7):403-405.[20]Kelly JT, Prasad AK, Wexler AS.Detailed flow patterns in the nasal cavity.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2000;89(1):323-337.[21]Anderson JR, Chiu DT, Jackman RJ,et al.Fabrication of topologically complex three-dimensional microfluidic systems in PDMS by rapid prototyping.Anal Chem. 2000;72(14): 3158-3164.[22]Luo Y, Zare RN.Perforated membrane method for fabricating three-dimensional polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic devices. Lab Chip. 2008;8(10):1688-1694. [23]D'Urso PS, Thompson RG, Atkinson RL,et al.Cerebrovascular biomodelling: a technical note.Surg Neurol. 1999;52(5): 490-500.[24]Wurm G, Tomancok B, Pogady P,et al.Cerebrovascular stereolithographic biomodeling for aneurysm surgery. Technical note.J Neurosurg. 2004;100(1):139-145.[25]Binder TM, Moertl D, Mundigler G,et al.Stereolithographic biomodeling to create tangible hard copies of cardiac structures from echocardiographic data: in vitro and in vivo validation.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35(1):230-237.[26]Sodian R, Loebe M, Hein A,et al.Application of stereolithography for scaffold fabrication for tissue engineered heart valves.ASAIO J. 2002;48(1):12-16. [27]Hockaday LA, Kang KH, Colangelo NW,et al.Rapid 3D printing of anatomically accurate and mechanically heterogeneous aortic valve hydrogel scaffolds.Biofabrication. 2012;4(3):035005.[28]黄明清,李杰,李翠玲,等.小口径脱细胞基质人工血管移植的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(1):61-63.[29]陆军,肖学钧,陈欣欣.脱细胞牛颈静脉血管支架的内皮化研究[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2009,25(5):346-349.[30]周敏,刘长建,卫志庆,等. bFGF预载脱细胞支架构建小口径人工血管的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2008,22(3):370-375.[31]周敏,刘长建,卫志庆,等.以肝素固化脱细胞支架构建的小口径抗凝人工血管[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(36): 7118-7121.[32]黄明清,李翠玲,李杰,等.小口径脱细胞基质人工血管移植后4周内膜增生的初步研究[J].国际医药卫生导报,2013,19(15): 2257-2260.[33]刘硕. 脱细胞脐血管作为小口径组织工程血管支架的探索研究[D]. 首都医科大学.2009.[34]Rotmans JI, Heyligers JM, Verhagen HJ,et al.In vivo cell seeding with anti-CD34 antibodies successfully accelerates endothelialization but stimulates intimal hyperplasia in porcine arteriovenous expanded polytetrafluoroethylene grafts. Circulation. 2005;112(1):12-18.[35]Suuronen EJ, Wong S, Kapila V,et al.Generation of CD133+ cells from CD133- peripheral blood mononuclear cells and their properties.Cardiovasc Res. 2006;70(1):126-135.[36]Pislaru SV, Harbuzariu A, Gulati R,et al.Magnetically targeted endothelial cell localization in stented vessels.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48(9):1839-1845.[37]Pislaru SV, Harbuzariu A, Agarwal G,et al.Magnetic forces enable rapid endothelialization of synthetic vascular grafts. Circulation. 2006;114(1 Suppl):1314-1318.[38]Hoffmann J, Paul A, Harwardt M,et al.Immobilized DNA aptamers used as potent attractors for porcine endothelial precursor cells.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;84(3):614-621.[39]Blindt R, Vogt F, Astafieva I,et al.A novel drug-eluting stent coated with an integrin-binding cyclic Arg-Gly-Asp peptide inhibits neointimal hyperplasia by recruiting endothelial progenitor cells.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(9):1786-1795.[40]李杰. 阿托伐他汀促进小口径人工血管移植后快速内皮化的初步研究[D] .中山大学.2010.[41]耿纪群,谢宗涛,蔡铭,等. 骨髓CD34+干细胞与单核细胞应用于组织工程小血管内皮化的比较[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012, 29(11): 2156-2158. |

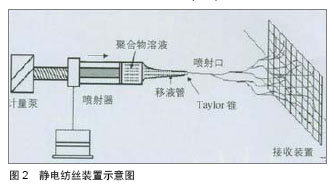
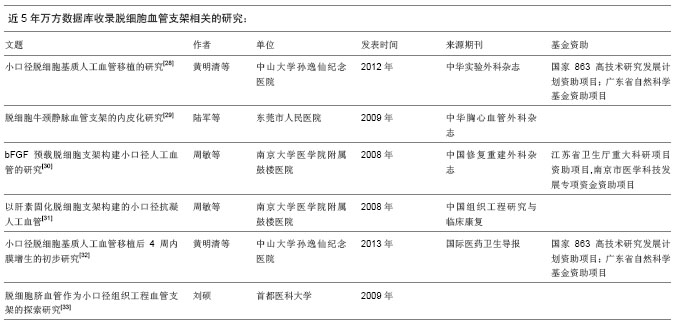
.jpg)